The modern era of communication has been radically transformed through the advent and advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Among the countless AI-powered chatbots, a noteworthy example is ChatGPT, a chatbot developed by the esteemed AI organization, OpenAI.
Its purpose is to interact with users, and its key component is the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), which generates responses resembling those of a human.
This article seeks to unravel the intricacies of GPT and explore its implementation in ChatGPT.
Understanding GPT in the Context of ChatGPT
In the domain of AI, GPT, or Generative Pre-trained Transformer, is an advanced language model that forms the core of various natural language processing (NLP) applications, including ChatGPT.
Its significance lies in its ability to assist ChatGPT in producing responses to user inquiries that mirror human-like conversation.
Implementation of GPT Technology in ChatGPT
ChatGPT harnesses the power of GPT technology to yield natural and coherent responses to user queries, achieved through deep learning model training and evaluation.
This innovative technology allows ChatGPT to generate text from vast datasets and respond to user questions in a manner akin to human conversation.
The underlying mechanism of ChatGPT’s training model is a technique known as Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF).
This involves a simulation of artificial conversations by humans, after which the AI adjusts its responses based on the accuracy of their reflection of authentic human dialogue.
This iterative process aims at enhancing ChatGPT’s ability to understand user queries more accurately.
Evolution of GPT: Tracing the Progress from GPT-1 to GPT-4
The GPT model has seen significant improvements since its inception, with each subsequent iteration refining the capabilities of its predecessor.

GPT-1
Launched in 2018, GPT-1 was the pioneer of the language model. It employed a single task-agnostic model with generative pre-training and discriminative fine-tuning, incorporating roughly 117 million parameters.
This model, trained on an expansive corpus of text, was capable of performing diverse tasks, including answering queries, text classification, semantic similarity assessment, and entailment determination.
GPT-2
In 2019, GPT-2 was introduced, building upon GPT-1’s achievements. Equipped with 1.5 billion parameters, GPT-2 aimed to comprehend words in context and elevate language processing capabilities.
It was employed for a range of NLP tasks such as question-answering system development, text generation and language translation.
GPT-3
The next breakthrough, GPT-3, was unveiled in 2020, boasting significant advancements in features and capabilities. With an impressive 175 billion parameters, it could intercept texts, answer complex queries, compose texts, and more.
In 2021, GPT-3 was integrated with ChatGPT, a popular AI chatbot, contributing to its massive success. The vast parameter count of GPT-3 facilitated a diverse range of tasks, including generating executable code and crafting poetry.
GPT-4
The latest version, GPT-4, was launched in March 2023 and introduced new potentials and functionalities in the AI market.
The most significant addition was the capability to accept visual input, allowing users to provide both text and image inputs. Although the exact number of parameters in GPT-4 is unknown, it is presumed to exceed that of GPT-3.
GPT-4 is a multi-modal model demonstrating human-level performance on various academic and professional benchmarks, including passing bar exams.
The evolutionary trajectory of GPT paints a promising picture, signaling its potential to attain unprecedented heights with continual advancements.
Comparing GPT-3.5 and GPT-4
GPT-4 has shown significant improvements over its predecessor, GPT-3.5, in terms of accuracy, reasoning capabilities, and handling of extensive prompts and conversations.
It operates as a data-to-text model, whereas GPT-3.5 is a text-to-text model. Additionally, GPT-4 can accept both text and visual inputs, while GPT-3.5 only accommodates text inputs.
Furthermore, GPT-4 exhibits enhanced creativity and coherence in generating stories, poems, or essays, whereas GPT-3.5, although creative, lacks the same coherence.
Applications of GPT in Chatbots and AI Assistants
The applications of GPT-based language models span a wide range of industries, contributing to increased productivity and benefits in areas like content creation and coding. Some notable applications include:
Customer Service
Companies such as H&M and Uber use GPT in their customer service departments to deliver fast and accurate responses, thereby enhancing productivity.
GPT-powered chatbots can swiftly comprehend and respond to customer queries in a manner resembling human conversation, alleviating the workload for customer service representatives.
Virtual Assistants
Virtual assistants such as Google Assistant, Apple Siri, and Be My Eyes employ GPT to deliver human-like responses and improve their language comprehension capabilities.
These assistants aid users in performing various tasks, including meeting scheduling, day planning, and setting reminders.
Content Creation
Businesses leverage GPT to create high-quality content for their websites, social media channels, blogs, and articles. GPT aids in generating content at a faster pace, saving time and resources, and enhancing overall quality by generating unique ideas.
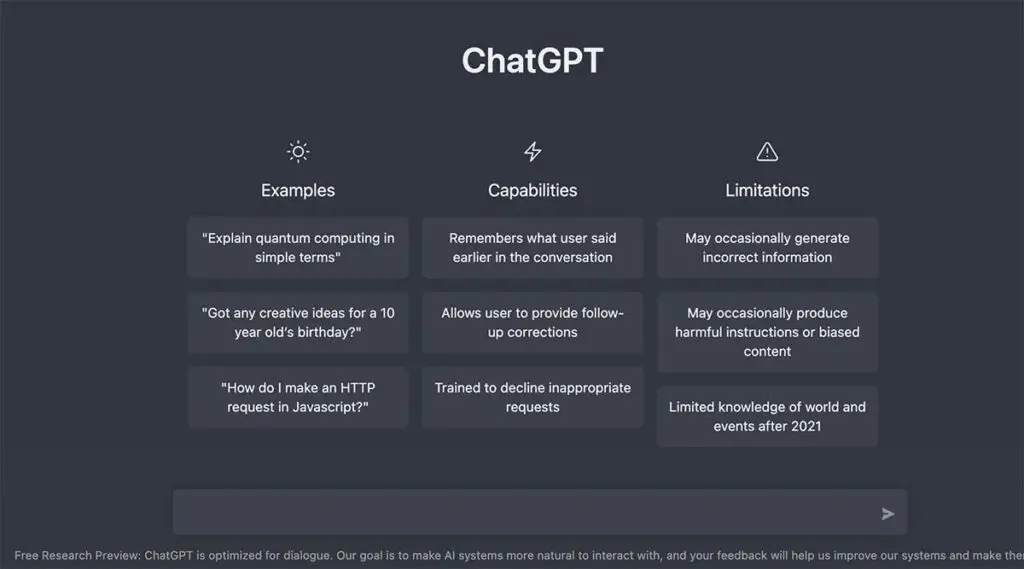
Identifying Limitations of ChatGPT
Like any technology, ChatGPT is not without its limitations. These include:
- Difficulty in Context Understanding: ChatGPT may struggle to comprehend the subtle nuances of human communication, particularly sarcasm and humor.
- Limited Knowledge: ChatGPT’s knowledge is confined to pre-2021 events.
- Algorithmic Biases: There have been instances of algorithmic biases in ChatGPT’s response generation.
- Training Data Constraints: Like many AI models, limitations in ChatGPT’s training data can pose significant drawbacks.
- Uneven Factual Accuracy: ChatGPT’s factual accuracy has also been found to be inconsistent.
Key Improvements of GPT-4 over GPT-3.5
GPT-4 has made significant strides over GPT-3.5 in various aspects.
It has shown remarkable advancements in understanding and processing complex mathematical and scientific concepts.
Its improved capability of handling longer prompts and conversations makes it suitable for tasks requiring extended interactions, such as chatbots or virtual assistants.
GPT-4’s enhanced reliability, creativity, and ability to process nuanced instructions mean that the model can generate more accurate and diverse outputs. It’s more flexible and adaptable to different use cases, and exhibits significant improvements in creative writing tasks.
Moreover, GPT-4’s multi-modal feature allows it to accept both text and visual inputs, widening its range of inputs and tasks. It’s also less prone to “hallucinating” compared to GPT-3.5, making it a more reliable and trustworthy model for various applications.
Uses of ChatGPT
ChatGPT’s versatility allows it to be used for more than human conversations.
It has been employed for various tasks, such as coding computer programs, composing music, drafting emails, summarizing articles, scripting social media posts, generating article titles, solving math problems, creating articles, blog posts, quizzes, rewording existing content, formulating product descriptions, assisting with job searches, asking trivia questions, and simplifying complex topics.
Alternatives to ChatGPT
Due to ChatGPT’s popularity, it can often be unavailable due to capacity constraints.
As a result, several alternatives have emerged. Google announced Bard, which draws information directly from the internet to provide the latest updates.
Microsoft incorporated ChatGPT functionality into Bing, enabling a chat mode for users with training data updated beyond 2021.
Other text generator alternatives include AI-Writer, ChatSonic, DeepL Write, Open Assistant, Perplexity AI, Rytr, and YouChat. Coding alternatives encompass CodeStarter, Amazon CodeWhisperer, CodeWP, OpenAI Codex, GitHub Copilot, and Tabnine.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GPT has revolutionized the landscape of AI-based conversational models, making strides in natural language understanding and generation.
While it has its limitations, continuous advancements, such as the transition from GPT-3.5 to GPT-4, offer promising prospects for further enhancing its capabilities and applications.
As AI technology continues to evolve, so too will our interactions with machines, further blurring the line between human and AI communication.




